Summary
The new Modular Services Platform (MSP) enables organizations to build flexible, scalable services through independent plugins. This framework allows developers to create extension services for business logic that integrate seamlessly with STEP while simplifying system maintenance through dedicated logging, localization, and configuration capabilities.
Details
The MSP framework is built around plugins — self-contained units of functionality that can be developed, deployed, and managed independently. This architecture allows developers to create extension services that communicate with STEP over HTTP to support decoupled service development. Developers can leverage a variety of plugin types to customize their services while operational efficiency is maintained from the Self-Service UI (SSUI) 'Modular Services' page.
For more information on MSP, including the progression from service development to deployment, refer to the 'Modular Service Platform API Guide' links in the 'Modular Service Platform' section of the Technical Documentation, available at [URL]/sdk or accessible from the Start Page. Also refer to the SSUI 'User guide' for details.
The following sections outline the functionality introduced with the 2025.3 Update.
Components
Modular services include the following components:
-
Extension framework is a Java library that enables developers to build STEP extensions that run as independent extension services outside the STEP system.
-
Extension engine is a runtime environment that hosts, manages, and runs the extension services, and provides HTTP endpoints for STEP to invoke.
-
STEP plugins can be deployed and configured in STEP to communicate with extension services.
In the SSUI, the 'Modular Services' page allows developers to configure, manage, and monitor plugin execution. All extension services are displayed, along with the status and the available actions (start, stop, and delete). Developers can also add a new service and check associated logs.
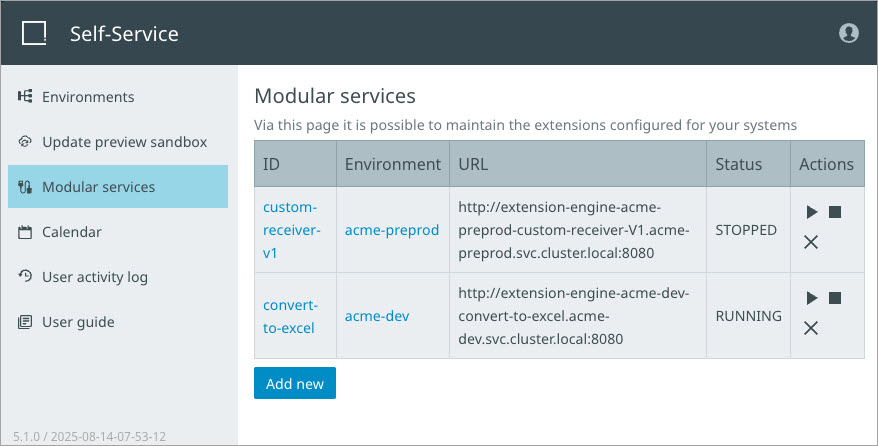
Plugin types
Developers can now create extension services using the following supported plugin types:
-
Delivery plugins deliver, process, or transform payloads received from STEP outbound integration endpoints. Payload objects are delivered to the next step in the process, for example, to integrate with an external system.
-
Inbound pre-processor plugins process or transform inbound messages before additional handling by the inbound integration endpoint, for example, to transform data from a custom format to a STEP-compatible format.
-
Outbound post-processor plugins process or transform outbound payloads after initial processing, for example, to transform or split messages before they are delivered.
-
Receiver plugins receive and manage inbound messages from external sources to an inbound integration endpoint, for example, to receive data from an event-streaming data platform or from a system not currently supported by STEP.
-
Business function plugins expose custom business logic as functions that can be called from a business function, for example, to convert to and from Excel.
Plugins in STEP Workbench
Once MSP plugins are defined and running in the SSUI, they are available for configuration in STEP Workbench. Developers can select and configure these plugins within the relevant IIEP, OIEP, or business function depending on their type.
-
Inbound integration endpoints - refer to the IIEP - Configure Pre-processor topic and the External Receiver topic, both in the Data Exchange documentation.
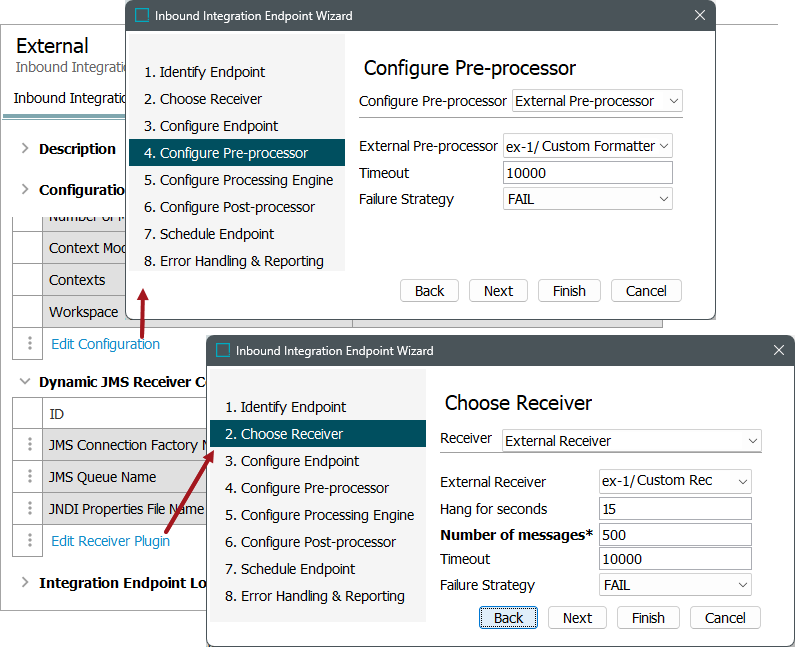
-
Outbound integration endpoints - refer to the OIEP - Event-Based - Output Templates Section topic, the OIEP - Select Objects - Output Templates Section topic, and the External Delivery Method topic, all in the Data Exchange documentation.
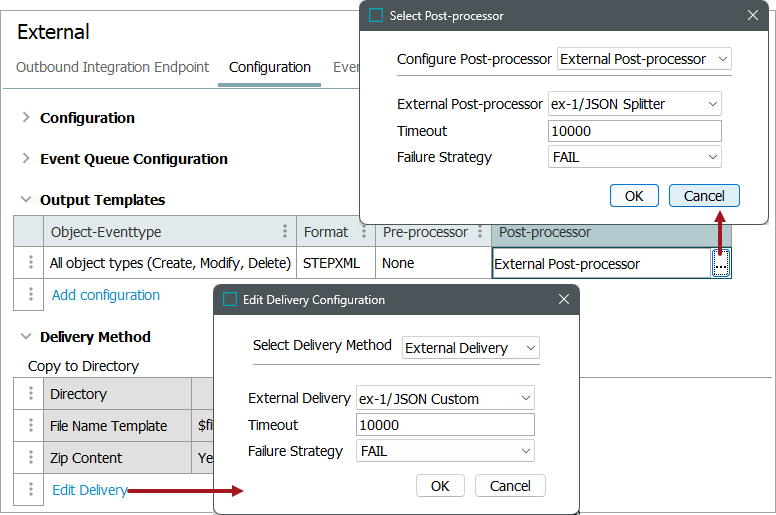
-
Business functions - refer to the External Business Operation topic in the Business Rules documentation.
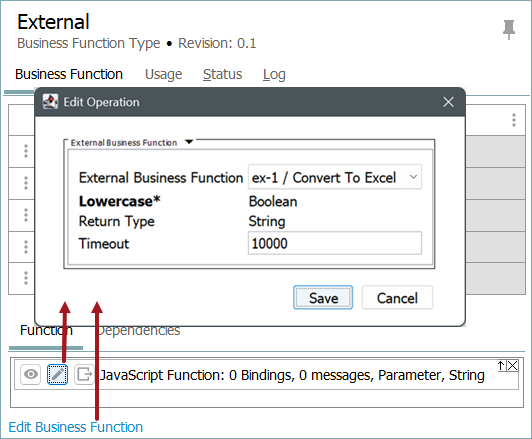
Explore further by clicking the video below. If it does not play as expected or you want to watch more videos, you can explore all our Product Updates videos on YouTube or within our Product Updates page on our corporate website.