Admins can configure STEP to automatically translate data using AI. By connecting to any Azure-hosted large language model (LLM) that supports the OpenAI Responses API , the asynchronous translation functionality can be used to send translation jobs to the LLM and receive back translated content automatically.
To configure Asynchronous Translation with AI, follow the steps described below:
-
Configure the system with the relevant component and licenses. Contact Stibo Systems to begin the process of enabling a license for your system.
-
Configure a gateway integration endpoint (GIEP).
There are two important settings when configuring the GIEP to enable async translation with AI.
-
Server URL - When populating the value for the 'Server URL' parameter, be sure to configure the server to point to an LLM that supports the OpenAI Responses API.
-
Auth Header value Function - To set up the GIEP, a business function must be set up for the purposes of authentication. Configuration of the business function is described in the next step.
For additional details about setting up gateway integration endpoints, refer to the Initial Setup for a Gateway Integration Endpoint topic in the Data Exchange documentation.
-
-
Configure a business function for authentication using the 'JavaScript Function' operation. When setting up the business function, three settings must be configured in the 'Edit Operation' window:
-
Binds - Use the 'Secret' bind. In this example, the variable name is 'apiKey' and 'Binds to' is set to 'Secret.' For more information on the 'Secret' bind type, refer to the relevant section in the Other Binds topic.
-
Return Type - Ensure the 'Return Type' is set to the Map<String.String> option.
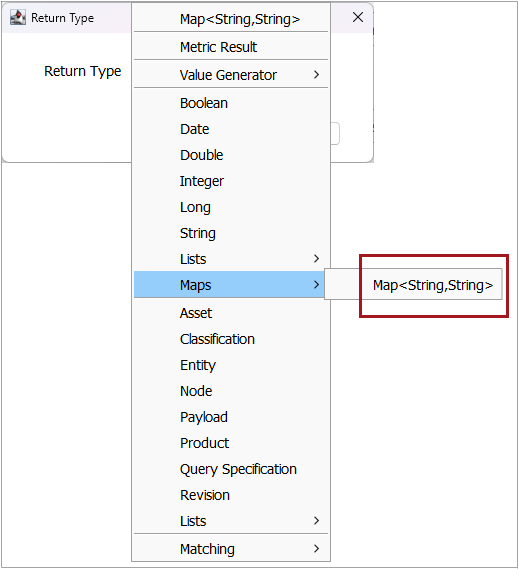
-
JavaScript - Set the 'JavaScript' field to include the text as shown in the screenshot and code snippet below:
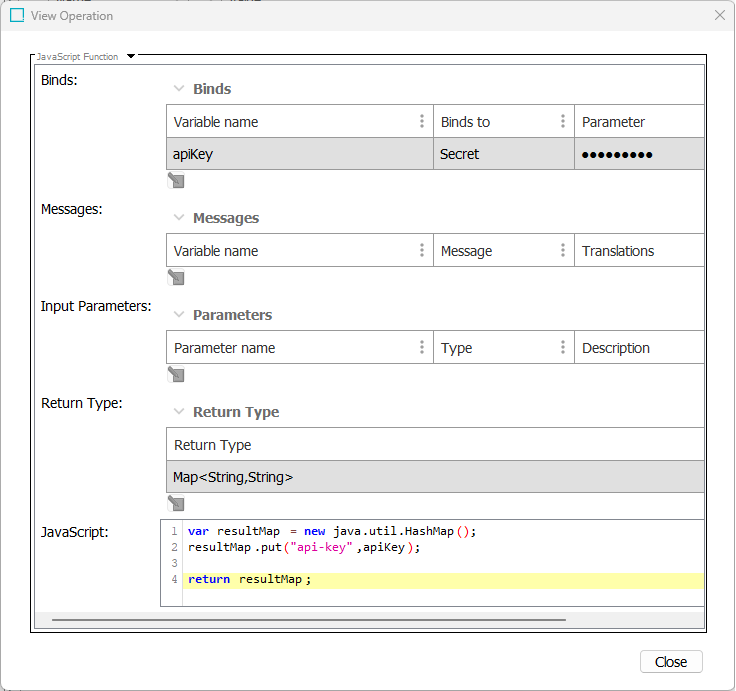 Copy
Copyvar resultMap = new java.util.HashMap();
resultMap.put("api-key",apiKey);
return resultMap;For more information on setting JavaScript functions, refer to the JavaScript Function Operation topic.
-
(Optional) Configure a transformation lookup table. Configuring a lookup table to select for the 'Language code lookup table' setting is only necessary if the ID of the STEP languages do not match to a language name the LLM understands. For instance, if the French language's ID in STEP is 'lang1,' a lookup table must be configured to transform 'lang1' to 'French.' It should be noted that, in some instances, an abbreviated language name, for example, 'Fre,' would be sufficient for an LLM to understand, and would not necessitate a lookup table. For more information on creating transformation lookup tables, refer to the 'Transformation Lookup Table for Language Codes' section of the Setting Up a Translation Configuration topic.
-
Configure an asynchronous translation service. For information about setting up an asynchronous translation service with AI, refer to the AI section of the Configuring an Asynchronous Translation Service topic.
-
Configure a business action to enable the asynchronous translation process to run. For information on how to configure this business rule, refer to the Business Rules for Asynchronous Translations topic.
With the asynchronous translation for AI functionality configured, return to the business function created in step three to run translations on the desired objects.
The AI prompt for translation is pre-defined in STEP. The snippet below shows the prompt being sent to the Azure-hosted LLM:
You are a translation engine. Your task is to translate text while preserving JSON structure.
Translate text values from source language to target language.
# Rules:
* Preserve tone, style, and idiomatic expressions.
* Return the result in exactly the same JSON structure as the input, only replacing the value fields in translatableValues with their translations.
* Do not remove or add any keys.
* Translate only the `value` fields inside `translatableValues`.
* Ensure the output has the same number of translatableValues as the input.
* Do not omit any translations.
F.ex. given the following input:
{
"setup": {
"sourceLanguage": "english",
"targetLanguage": "danish",
"batchId": "b1"
},
"requests": [
{
"id": "P1",
"contextualValues": [],
"translatableValues": [
{ "value": { "id": "1", "value": "Hello" } },
{ "value": { "id": "2", "value": "World" } }
]
}
]
}
Should generate the following output:
{
"setup": {
"sourceLanguage": "english",
"targetLanguage": "danish",
"batchId": "b1"
},
"requests": [
{
"id": "P1",
"contextualValues": [],
"translatableValues": [
{ "value": { "id": "1", "value": "Hallo" } },
{ "value": { "id": "2", "value": "Verden" } }
]
}
]
}
# Formatting Instructions:
* Preserve all placeholders, tags, and special characters.
* Maintain line breaks and structure.
* Do not translate brand names or codes.The prompt can be amended if needed. For information about making changes to the translation prompts, consult with a Stibo Systems technical representative.
For more information on the asynchronous translation functionality, refer to the Asynchronous Translations topics.